Guangdong LiYou Steel Structure Engineering Co., Ltd. +8619147784007 liyousteelstructure@outlook.com
Q: How deep should foundations be for steel buildings?
A: Typically 1-3m, depending on soil and frost line (deeper for seismic zones).
Q: Can I reuse old foundations?
A: Only after structural assessment (we provide evaluation services).
Q: What's the curing time before steel erection?
A: 7-28 days (depending on concrete mix design).
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
Workshop
Online technical support, Onsite Installation, Onsite Training, Onsite Inspection, Free spare parts, Return and Replacement, Other
graphic design, 3D model design, total solution for projects, Cross Categories Consolidation, Others
Steel Workshop, garage shed, storage closet, buildings prefab workshop, steel warehouse, Hotel, Villa, Apartment, Office Building, Hospital, School, Mall, Sports Venues, Leisure Facilities, supermarket, Warehouse, Workshop, Park, Farmhouse, Courtyard, Other, Kitchen, Bathroom, Home Office, Living Room, Bedroom, Dining, Babies and kids, Outdoor, Storage & Closet, Exterior, Wine Cellar, Entry, Hall, Home Bar, Staircase, Basement, Garage & Shed, Gym, Laundry
Modern
Guangdong, China
Lifetime
engineer guidance
Liyou
LY001
CE Certification
Industrial Commercial
C.Z Shape Steel Channel
Sliding Door
Customized Color
Sandwich Panel Optional
Aluminum Alloy Sliding Window
SAP2000/AutoCAD /PKPM /3D3S/TEKLA
Hot Dip Galvanized
25-60 days
Single item
1X1X1 cm
1.000 kg
| Foundation Type | Best For | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spread Footings | Light-mid weight structures | Low cost, simple construction | Weak in expansive soils |
| Pile Foundations | Heavy loads/poor soil | High load capacity | Expensive, requires special equipment |
| Mat Foundations | High-rise buildings | Even load distribution | High concrete usage |
| Grade Beams | Perimeter support | Resists differential settlement | Limited to medium loads |
Load Calculations:
Dead loads (structure weight)
Live loads (occupancy/equipment)
Environmental loads (wind/seismic)
Soil Bearing Capacity:
Clay: 50-200 kPa
Sand: 100-300 kPa
Rock: 500+ kPa
Anchor Bolt Planning:
Standard sizes: M20-M64
Embedment depth = 12-25×bolt diameter
Site Preparation (excavation, compaction)
Formwork Installation (±5mm tolerance)
Rebar Cage Placement (cover ≥50mm)
Anchor Bolt Positioning (jig required)
Concrete Pouring (C25-C35 grade)
Grouting (non-shrink, 25-50mm layer)
| Component | Design Standard |
|---|---|
| Footings | ACI 318 / EN 1992 |
| Anchor Bolts | AISC 360 / EN 1993 |
| Soil Testing | ASTM D1586 / ISO 22476 |
✖ Underestimating uplift forces
✖ Poor bolt alignment (>3mm deviation)
✖ Inadequate drainage around foundation
✖ Ignoring frost depth requirements
| Foundation Type | Cost/m² (USD) |
|---|---|
| Spread Footing | $120-$180 |
| Pile Foundation | $300-$600 |
| Mat Foundation | $250-$400 |
Pro Tip: Foundation costs typically represent 15-25% of total steel structure budget.
Turnkey Solutions (design to construction)
Anchor Bolt Templates (laser-cut, ±1mm accuracy)
3D Modeling (Tekla Structures integration)
Global Compliance (IBC, Eurocode, GB standards)
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
| No. | Components | Specification | ||
| Embedded Parts | ||||
| 1 | Anchor Bolt | M24 | ||
| 2 | High Strength Bolt | M20,10.9S | ||
| 3 | Common Bolt | M16 | ||
| 4 | Galvanized Bolt | M12 | ||
| 5 | Shear Nail | M16 | ||
| 6 | Tir rod | ∅32*2.5 | ||
| Main Steel Structure Parts | ||||
| 1 | Steel Column (Q355B) | H550*300*10*16 | ||
| 2 | Wind Column (Q355B) | H400*220*6*10 | ||
| 3 | Roof Frame Beam (Q355B) | H900~500*220*10*12 H500~650*220*8*12 | ||
| 4 | Crane Beam (Q355B) | H650*320/240*10*16/14 | ||
| 5 | Tie Bar(Q235B) | ∅168*4.0 | ||
| 6 | Horizontal Brace (Q235B) | ∅168*4.0 | ||
| 7 | Column Brace (Q235B) | ∅25 | ||
| 8 | Angle Brace (Q235B) | L63*5.0 | ||
| 9 | Roof Purlin (Galvanized) | Z280*80*20*2.5 | ||
| 10 | Wall Purlin (Galvanized) | C250*75*20*2.5 | ||
| 11 | Connecting Plate | 6mm-30mm | ||
| Other Steel Structure Parts | ||||
| 1 | Roof Panel | 50mm Rock wool Sandwich panel | ||
| 2 | Wall Panel | 50mm Rock wool Sandwich panel | ||
| 3 | Gutter | 2mm Galvanized Steel Plate | ||
| 4 | Down Pipe | PVC160 (Including parts) | ||
| 5 | Trimming | Color steel 0.5mm Gavanized steel panel | ||
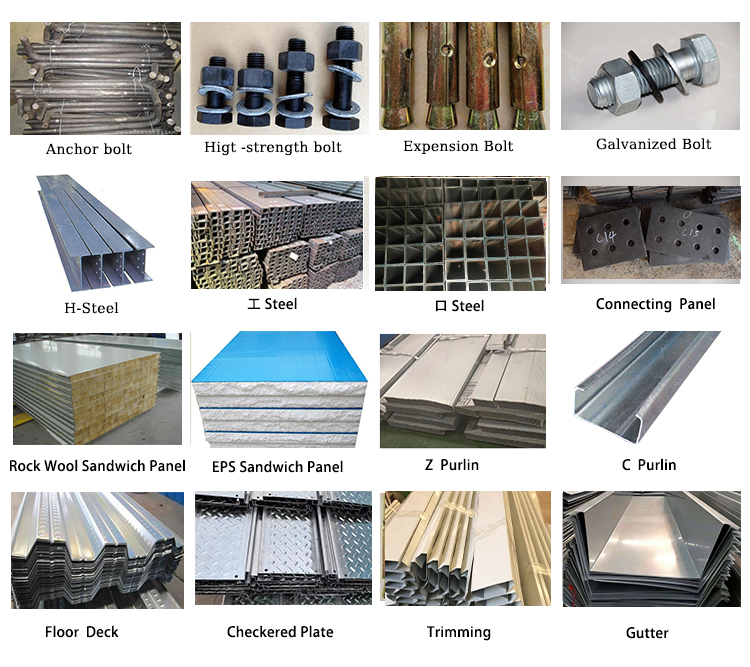









A steel construction foundation refers to the foundation of a building or structure that is designed to support the weight and load of a steel-framed structure. Steel foundations typically consist of steel beams, plates, or steel piles that are anchored into the ground to ensure stability and durability. These foundations are used in various types of construction, including commercial, industrial, and residential projects.
Steel is used for construction foundations due to its:
Strength: Steel provides excellent load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for supporting large and heavy structures.
Durability: Steel is resistant to pests, decay, and environmental factors such as moisture, which can affect other materials like wood.
Flexibility: Steel foundations can be customized to suit specific site conditions and design requirements, providing versatile solutions for various building types.
Quick Installation: Steel components can be pre-fabricated off-site and assembled quickly, reducing construction time.
There are several types of steel foundations commonly used in construction:
Steel Plate Foundations: Steel plates are installed directly on the ground to create a stable base for the building.
Steel Pile Foundations: Steel piles are driven deep into the ground to provide additional support for buildings in areas with weak soil or high water tables.
Steel Beam Foundations: Steel beams are used to form a network of support for the structure, typically combined with concrete or other materials for reinforcement.
Mat Foundations: A large steel-reinforced slab that spreads the load evenly across a larger area, often used for heavy or tall buildings.
The key benefits of using steel foundations include:
Long-Term Durability: Steel is highly resistant to environmental damage, including moisture, termites, and weather conditions.
Higher Load-Bearing Capacity: Steel provides superior strength compared to other materials like wood or concrete, making it suitable for supporting large or multi-story buildings.
Adaptability: Steel foundations can be tailored to the unique requirements of a site, offering greater flexibility in challenging soil conditions.
Cost Efficiency: Although steel foundations can have a higher initial cost, their longevity and low maintenance needs can result in significant cost savings over time.
Steel construction foundations are highly durable and can last 50 years or more, depending on factors such as the quality of the steel, environmental conditions, and maintenance. Steel is resistant to many of the issues that affect other foundation materials, such as rotting, pests, and rust, especially when coated with protective materials like galvanisation.
Yes, steel foundations are suitable for various types of construction projects, including:
Commercial buildings: Offices, retail centers, and shopping malls.
Industrial buildings: Factories, warehouses, and manufacturing plants.
Residential buildings: Steel-framed homes or multi-story residential buildings.
Infrastructure projects: Bridges, piers, and elevated structures.
Steel foundations are particularly beneficial in areas with challenging soil conditions, such as weak or expansive soils.
Both steel foundations and concrete foundations are strong, but they offer different advantages:
Strength: Steel foundations typically offer greater flexibility and higher load-bearing capacity than concrete, especially in large-scale construction.
Durability: Steel is more resistant to moisture, pests, and environmental degradation than concrete, making it a better choice for areas prone to corrosion or water damage.
Installation Speed: Steel foundations often require less time to install, as steel components are pre-fabricated off-site, while concrete foundations require curing time.
Cost: Concrete foundations are often more affordable in the short term, but steel foundations offer long-term cost benefits due to their durability and reduced maintenance needs.
The cost of steel foundations depends on several factors, including:
Project Size: Larger buildings or structures will require more materials and labor, increasing costs.
Site Conditions: Challenging soil conditions, such as soft or uneven ground, may require more extensive steel foundation work, increasing the overall cost.
Design Requirements: Custom designs or specialized steel components can raise costs, especially for unique or complex projects.
Materials Used: High-quality or specialized steel materials, such as galvanised steel, can increase the price of the foundation.
Yes, steel foundations are an excellent choice for areas with poor soil conditions. Steel piles, for example, can be driven deep into the ground to anchor the building to solid bedrock or more stable soil layers. Steel foundations provide superior support in areas with soft, expansive, or unstable soil, where traditional concrete foundations might not be feasible or cost-effective.
Steel foundations generally require little maintenance, but regular inspections are recommended to ensure their integrity:
Inspect for corrosion: If the steel is exposed to harsh conditions or direct moisture, inspect for signs of rust or corrosion.
Check for structural damage: Ensure that no components of the foundation, such as steel beams or plates, are damaged or shifted.
Protective Coatings: Reapply protective coatings or galvanisation if necessary to prevent rust or corrosion in areas where the steel is exposed to the elements.
| Foundation Type | Best For | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spread Footings | Light-mid weight structures | Low cost, simple construction | Weak in expansive soils |
| Pile Foundations | Heavy loads/poor soil | High load capacity | Expensive, requires special equipment |
| Mat Foundations | High-rise buildings | Even load distribution | High concrete usage |
| Grade Beams | Perimeter support | Resists differential settlement | Limited to medium loads |
Load Calculations:
Dead loads (structure weight)
Live loads (occupancy/equipment)
Environmental loads (wind/seismic)
Soil Bearing Capacity:
Clay: 50-200 kPa
Sand: 100-300 kPa
Rock: 500+ kPa
Anchor Bolt Planning:
Standard sizes: M20-M64
Embedment depth = 12-25×bolt diameter
Site Preparation (excavation, compaction)
Formwork Installation (±5mm tolerance)
Rebar Cage Placement (cover ≥50mm)
Anchor Bolt Positioning (jig required)
Concrete Pouring (C25-C35 grade)
Grouting (non-shrink, 25-50mm layer)
| Component | Design Standard |
|---|---|
| Footings | ACI 318 / EN 1992 |
| Anchor Bolts | AISC 360 / EN 1993 |
| Soil Testing | ASTM D1586 / ISO 22476 |
✖ Underestimating uplift forces
✖ Poor bolt alignment (>3mm deviation)
✖ Inadequate drainage around foundation
✖ Ignoring frost depth requirements
| Foundation Type | Cost/m² (USD) |
|---|---|
| Spread Footing | $120-$180 |
| Pile Foundation | $300-$600 |
| Mat Foundation | $250-$400 |
Pro Tip: Foundation costs typically represent 15-25% of total steel structure budget.
Turnkey Solutions (design to construction)
Anchor Bolt Templates (laser-cut, ±1mm accuracy)
3D Modeling (Tekla Structures integration)
Global Compliance (IBC, Eurocode, GB standards)
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
| No. | Components | Specification | ||
| Embedded Parts | ||||
| 1 | Anchor Bolt | M24 | ||
| 2 | High Strength Bolt | M20,10.9S | ||
| 3 | Common Bolt | M16 | ||
| 4 | Galvanized Bolt | M12 | ||
| 5 | Shear Nail | M16 | ||
| 6 | Tir rod | ∅32*2.5 | ||
| Main Steel Structure Parts | ||||
| 1 | Steel Column (Q355B) | H550*300*10*16 | ||
| 2 | Wind Column (Q355B) | H400*220*6*10 | ||
| 3 | Roof Frame Beam (Q355B) | H900~500*220*10*12 H500~650*220*8*12 | ||
| 4 | Crane Beam (Q355B) | H650*320/240*10*16/14 | ||
| 5 | Tie Bar(Q235B) | ∅168*4.0 | ||
| 6 | Horizontal Brace (Q235B) | ∅168*4.0 | ||
| 7 | Column Brace (Q235B) | ∅25 | ||
| 8 | Angle Brace (Q235B) | L63*5.0 | ||
| 9 | Roof Purlin (Galvanized) | Z280*80*20*2.5 | ||
| 10 | Wall Purlin (Galvanized) | C250*75*20*2.5 | ||
| 11 | Connecting Plate | 6mm-30mm | ||
| Other Steel Structure Parts | ||||
| 1 | Roof Panel | 50mm Rock wool Sandwich panel | ||
| 2 | Wall Panel | 50mm Rock wool Sandwich panel | ||
| 3 | Gutter | 2mm Galvanized Steel Plate | ||
| 4 | Down Pipe | PVC160 (Including parts) | ||
| 5 | Trimming | Color steel 0.5mm Gavanized steel panel | ||










A steel construction foundation refers to the foundation of a building or structure that is designed to support the weight and load of a steel-framed structure. Steel foundations typically consist of steel beams, plates, or steel piles that are anchored into the ground to ensure stability and durability. These foundations are used in various types of construction, including commercial, industrial, and residential projects.
Steel is used for construction foundations due to its:
Strength: Steel provides excellent load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for supporting large and heavy structures.
Durability: Steel is resistant to pests, decay, and environmental factors such as moisture, which can affect other materials like wood.
Flexibility: Steel foundations can be customized to suit specific site conditions and design requirements, providing versatile solutions for various building types.
Quick Installation: Steel components can be pre-fabricated off-site and assembled quickly, reducing construction time.
There are several types of steel foundations commonly used in construction:
Steel Plate Foundations: Steel plates are installed directly on the ground to create a stable base for the building.
Steel Pile Foundations: Steel piles are driven deep into the ground to provide additional support for buildings in areas with weak soil or high water tables.
Steel Beam Foundations: Steel beams are used to form a network of support for the structure, typically combined with concrete or other materials for reinforcement.
Mat Foundations: A large steel-reinforced slab that spreads the load evenly across a larger area, often used for heavy or tall buildings.
The key benefits of using steel foundations include:
Long-Term Durability: Steel is highly resistant to environmental damage, including moisture, termites, and weather conditions.
Higher Load-Bearing Capacity: Steel provides superior strength compared to other materials like wood or concrete, making it suitable for supporting large or multi-story buildings.
Adaptability: Steel foundations can be tailored to the unique requirements of a site, offering greater flexibility in challenging soil conditions.
Cost Efficiency: Although steel foundations can have a higher initial cost, their longevity and low maintenance needs can result in significant cost savings over time.
Steel construction foundations are highly durable and can last 50 years or more, depending on factors such as the quality of the steel, environmental conditions, and maintenance. Steel is resistant to many of the issues that affect other foundation materials, such as rotting, pests, and rust, especially when coated with protective materials like galvanisation.
Yes, steel foundations are suitable for various types of construction projects, including:
Commercial buildings: Offices, retail centers, and shopping malls.
Industrial buildings: Factories, warehouses, and manufacturing plants.
Residential buildings: Steel-framed homes or multi-story residential buildings.
Infrastructure projects: Bridges, piers, and elevated structures.
Steel foundations are particularly beneficial in areas with challenging soil conditions, such as weak or expansive soils.
Both steel foundations and concrete foundations are strong, but they offer different advantages:
Strength: Steel foundations typically offer greater flexibility and higher load-bearing capacity than concrete, especially in large-scale construction.
Durability: Steel is more resistant to moisture, pests, and environmental degradation than concrete, making it a better choice for areas prone to corrosion or water damage.
Installation Speed: Steel foundations often require less time to install, as steel components are pre-fabricated off-site, while concrete foundations require curing time.
Cost: Concrete foundations are often more affordable in the short term, but steel foundations offer long-term cost benefits due to their durability and reduced maintenance needs.
The cost of steel foundations depends on several factors, including:
Project Size: Larger buildings or structures will require more materials and labor, increasing costs.
Site Conditions: Challenging soil conditions, such as soft or uneven ground, may require more extensive steel foundation work, increasing the overall cost.
Design Requirements: Custom designs or specialized steel components can raise costs, especially for unique or complex projects.
Materials Used: High-quality or specialized steel materials, such as galvanised steel, can increase the price of the foundation.
Yes, steel foundations are an excellent choice for areas with poor soil conditions. Steel piles, for example, can be driven deep into the ground to anchor the building to solid bedrock or more stable soil layers. Steel foundations provide superior support in areas with soft, expansive, or unstable soil, where traditional concrete foundations might not be feasible or cost-effective.
Steel foundations generally require little maintenance, but regular inspections are recommended to ensure their integrity:
Inspect for corrosion: If the steel is exposed to harsh conditions or direct moisture, inspect for signs of rust or corrosion.
Check for structural damage: Ensure that no components of the foundation, such as steel beams or plates, are damaged or shifted.
Protective Coatings: Reapply protective coatings or galvanisation if necessary to prevent rust or corrosion in areas where the steel is exposed to the elements.
content is empty!